-
Time:4/2/2025
-
Time:3/31/2025
-
Time:2/19/2025

- CONTACT US
- [email protected]
Company News
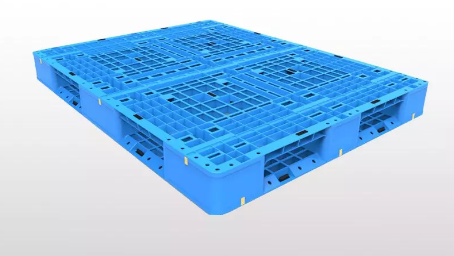
What Are Plastic Pallets Made Of
 Time:4/2/2025
Time:4/2/2025 129
129Share:
Plastic pallets are typically made from various types of plastic materials, each chosen for its durability, load-bearing capacity, and resistance to environmental factors. The most common materials used in plastic pallet manufacturing include:

1. High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
Usage: Widely used in reusable and export pallets due to its long lifespan and recyclability.
Pros: Resistant to chemicals, easy to clean, and lightweight.
Cons: Can be more expensive than other plastic types.
2. Polypropylene (PP)
Usage: Used in heavy-duty and hygienic pallets, especially in industries like pharmaceuticals and food.
Pros: High strength and resistance to high temperatures.
Cons: More brittle compared to HDPE and may crack under extreme impact.
3. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Usage: Less common but sometimes used for specialty pallets in corrosive environments.
Pros: Fire-resistant and resistant to chemical corrosion.
Cons: Heavier than HDPE and PP, making it less desirable for logistics.
4. Recycled Plastics (Mixed Plastic Composites)
Usage: Used in one-way shipping pallets and budget-friendly solutions.
Pros: Environmentally friendly, cost-effective.
Cons: Quality and durability can vary based on material composition.
Manufacturing Processes
Injection Molding – Creates highly durable, precision-designed pallets.
Blow Molding – Produces hollow, lightweight, and impact-resistant pallets.
Thermoforming – Used for lightweight, disposable, or nestable pallets.
Compression Molding – Commonly used for recycled plastic pallets.